Intro to Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds such as hydrocarbons, Petroleum, Functional group compounds, Bio molecular compounds etc. For Biomolecular compounds will be on the biochemistry section. Organic chemistry is very wide and have many interesting things. It's the basic for something like Pharmaceuticals which have many compounds with many functional groups. The study of organic chemistry needs some basics about writing line and condensed formula of carbon compounds. Note : These carbon compounds are not Organic : H2CO3 (Carbonic acid), CO2(Carbon Dioxide) ,CO3(2-)(Carbonate compounds), HCO3(1-)(Bicarbonate Compounds)

Organic compounds basics (Hydrocarbons)
1.Alkanes
Alkane is a kind of hydrcarbon compounds with a formula of CnH2n+2. every carbon atom of alkane have single bonds between them. They are mostly Petroleum matters. Alkanes don't have high reactivity because of the single bonds. The larger amount of carbon atom, the higher the melting and boiling points is. 1-4 Carbon atoms the alkane will be in gas state. 5-17 carbon atoms, the alkane will be in liquid state. 18 or more carbon atoms, the alkane will be in solid state. Naming the Alkane will be named the prefixes first acccording to the number of carbon atoms and then the -ane. here are some common prefixes
1C Meth- Methane
2C Eth- Ethane
3C Pro- Propane
4C But- Butane
5C Pent- Pentane
6C Hex- Hexane
7C Hept- Heptane
8C Oct- Octane
9C Non- Nonane
10C Dec- Decane

2.Alkyl
Alkyl have the formula of CnH2n+1. Alkyl mostly attached to other functional groups such as hydroxyl group or carboxyl group. Name the alkyl by prefixes and -yl.
1C Meth- Methyl CH3-
2C Eth- Ethyl C2H5-
3C Pro- Proyl C3H7-
4C But- Butyl C4H9-
5C Pent- Pentyl
6C Hex- Hexyl
7C Hept- Heptyl
8C Oct- Octyl
9C Non- Nonyl
10C Dec- Decyl
3.Alkene
Alkene have the formula of CnH2n. Alkenes have a double bond between 1 pair of carbon atoms. Alkene have a higher reactivity than alkane because of the double bonds and have much lower B.P and M.P than alkanes Eg. C2H6 B.P.=-89 Celsius. C2H4 B.P.=-103.4 Celsius.Name the alkene by prefixes and -ene.
4.Alkynes
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between a pair of carbon atoms. Alkynes have a formula of CnH2n-2. Alkynes have a very low B.P. and F.P. and they have a high reactivity. Name the prefix and then -yne.

- The full structure and formula of Hydrocarbon compounds is alkane. every double bonds and Closed Cyclic hydrocarbons will take away 2 hydrogens from Alkane and every triple bonds take away 4 hydrogen bonds from alkane. example: 3Carbon Hydrocarbon , Alkane: C3H8, Cycloalkane and alkene: C3H6 and Alkyne : C3H4.
- Hydrocarbons in compounds with functional group determines the Physical properties such as Melting Point, Boiling Point
- Bigger Hydrocarbons have higher Melting Point and Boiling Point (More Carbons, The higher the melting and freezing points). Double or triple bonds can lower the Boiling and Melting point
Organic Functional Group
- Some Organic Compounds have functional groups. Some of them have 1 and some of them have more than 1. Functional group determines their chemical properties. Here are some Functional groups.
1.Hydroxyl : Hydroxyl grop has a structure of R-OH (R stands for Alkyl group) and needs an alkyl to be attached. Hydroxyl make compounds called Alcohols. Name the Alkyl first and then Alcohol of the prefix according to how many carbons and then -nol. Hydroxyl attracts water so most alcohols is water soluble. Smaller Hydroxyls is more water soluble. Don't Confuse with hydroxide. Hydroxyl is for organic compounds only, while hydroxide is a polyatomic ion (OH(-1)) for ionic compounds. Examples: CH3-OH is named Methyl Alcohol or Methanol, C2H5-OH is named ethyl Alcohol or ethanol. There are other alcohols such as Gylcerol (C3H8O3)

2. Aldehydes : Many organic compounds have aldehyde. Aldehydes have a structure of R-CHO Some Aldehydes have a strong odour. Smaller aldehydes is more water soluble. Naming aldehydes, ketones and Carboxyls are slightly different from hydrocarbon compounds by the prefixes of 1 carbon compound will be form- and 2 carbons compounds is acet-. Name the Prefix first by according to how many carbons and then aldehyde Counting carbons in aldehyde includes the carbon in the functional group. example CH2O is named Formaldehyde, CH3-CHO is named Acetaldehyde.
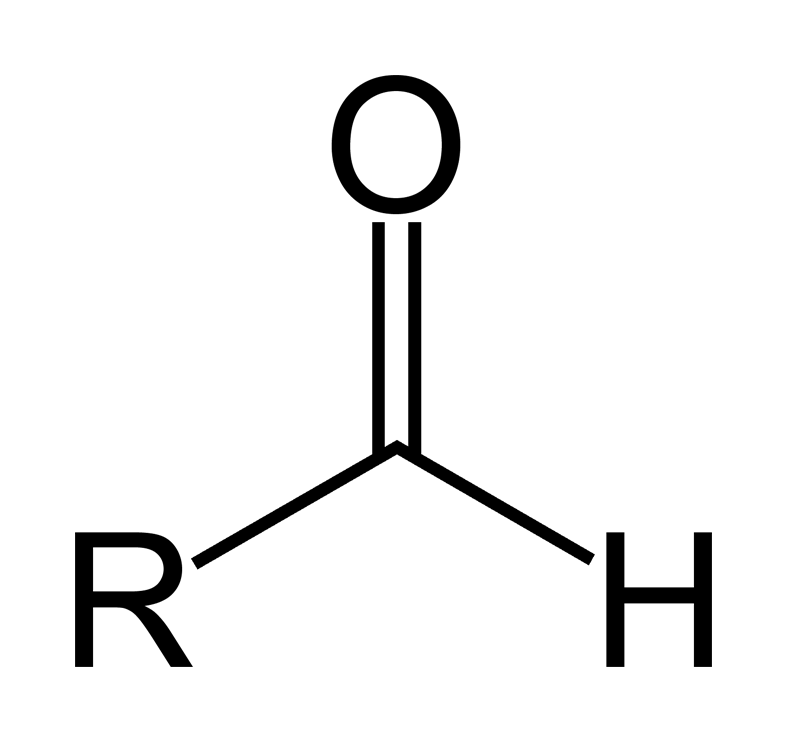
3. Ketones : Ketones have a very similar formula to aldehyde. It's Formula is R-CO-R', So there can be up to 2 alkyls in one Ketone. Counting Carbons for naming ketone does NOT include the carbon in the Functional Group. Name the Compound with ketone By prefix and then -one. Example : CH3-CO-CH3 is named Acetone.

4. Carboxyl : Carboxyl has a very similar formula to Aldehyde. It's Formular is R-COOH. Carboxyl produce compounds called Carboxylic acid. Counting carbon for naming includes carbon in the functional group. Name by prefix then -ic acid. Some of them have special name, Mostly Fatty acids dosen't have prefixes, they have a specific name. Carboxyl is also a functional group for fatty acid. Every acid with Caboxyl is considered Organic Acid. Most of them when dissociates give an ion. There is one special carboxylic acid, HCOOH is a carboxylic acid not aldehyde and it's named Formic Acid . Example : CH3COOH (Acetic Acid), C17H35COOH (Stearic Acid).
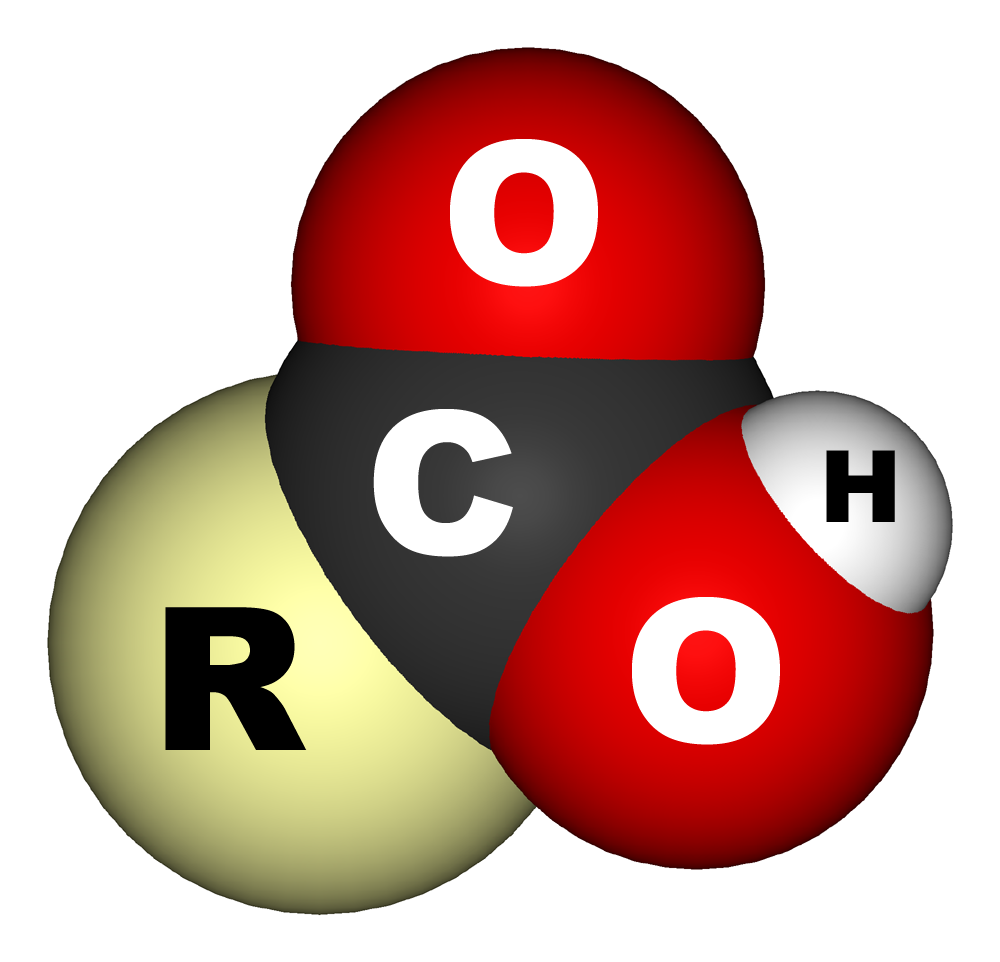
5. Sulfhydryl : Sulfhydryl has a structure of R-SH. Sulfhydryl produces a compound called Thiol. Sulfhydryl has a strong smell and some are not water soluble. Some Amino acid have sulfhydryl and 2 sulfurs can bond with each other to make a bond called Disulfide bond. Name the Sulfhydryl compound by Naming the alkyl and then thiol. Example: CH3SH (Methyl Thiol).

6.Amine : Amine has a structure of R-NH2 (Primary Amine). There are more structure of amine which is Secondary amine (R-NH-R') and tertiary amine (R-N(R')-R''). Amine makes many compound with other functional groups such as amino acids which is amine with carboxyl. All amino acids have a name. Amine also Acts as a base. If you are naming the amine compound with an alkyl, name the alkyl first then amine. Example : C2H5-NH2 (Ethyl Amine). Here are some amino acids : Alanine, Threonine.

- Here are just some Basic Functional group, There can be more functional group, Some of them are combined function groups with other functional groups of hydrocarbons.


Alkane is a kind of hydrcarbon compounds with a formula of CnH2n+2. every carbon atom of alkane have single bonds between them. They are mostly Petroleum matters. Alkanes don't have high reactivity because of the single bonds. The larger amount of carbon atom, the higher the melting and boiling points is. 1-4 Carbon atoms the alkane will be in gas state. 5-17 carbon atoms, the alkane will be in liquid state. 18 or more carbon atoms, the alkane will be in solid state. Naming the Alkane will be named the prefixes first acccording to the number of carbon atoms and then the -ane. here are some common prefixes
1C Meth- Methane
2C Eth- Ethane
3C Pro- Propane
4C But- Butane
5C Pent- Pentane
6C Hex- Hexane
7C Hept- Heptane
8C Oct- Octane
9C Non- Nonane
10C Dec- Decane

2.Alkyl
Alkyl have the formula of CnH2n+1. Alkyl mostly attached to other functional groups such as hydroxyl group or carboxyl group. Name the alkyl by prefixes and -yl.
1C Meth- Methyl CH3-
2C Eth- Ethyl C2H5-
3C Pro- Proyl C3H7-
4C But- Butyl C4H9-
5C Pent- Pentyl
6C Hex- Hexyl
7C Hept- Heptyl
8C Oct- Octyl
9C Non- Nonyl
10C Dec- Decyl
3.Alkene
Alkene have the formula of CnH2n. Alkenes have a double bond between 1 pair of carbon atoms. Alkene have a higher reactivity than alkane because of the double bonds and have much lower B.P and M.P than alkanes Eg. C2H6 B.P.=-89 Celsius. C2H4 B.P.=-103.4 Celsius.Name the alkene by prefixes and -ene.
4.Alkynes
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between a pair of carbon atoms. Alkynes have a formula of CnH2n-2. Alkynes have a very low B.P. and F.P. and they have a high reactivity. Name the prefix and then -yne.
5.Aromatic Hydrocarbons Compounds
In organic chemistry there are not many Aromatic Hydrocarbon compound. The simplest compound is Benzene (C6H6). Aromatic compounds can absord UV. Every compounds that have benzene in it's Structure, it's considered Aromatic Compounds. Some examples are : Benzene (C6H6), Napthalene (C10H8).

6.Other Hydrocarbon Compounds


6.Other Hydrocarbon Compounds
There can be much more hydrocarbon compounds that their formula does not fit in the categories above. Mostly they are synthetic. As long that their formula and composition is only Carbon and Hydrogen, They are considered Hydrocarbon Compounds
- All Hydrocarbon Compounds are nonpolar, so they won't dissolve in water but they will dissolve in other nonpolar compounds.
- The full structure and formula of Hydrocarbon compounds is alkane. every double bonds and Closed Cyclic hydrocarbons will take away 2 hydrogens from Alkane and every triple bonds take away 4 hydrogen bonds from alkane. example: 3Carbon Hydrocarbon , Alkane: C3H8, Cycloalkane and alkene: C3H6 and Alkyne : C3H4.
- Hydrocarbons in compounds with functional group determines the Physical properties such as Melting Point, Boiling Point
- Bigger Hydrocarbons have higher Melting Point and Boiling Point (More Carbons, The higher the melting and freezing points). Double or triple bonds can lower the Boiling and Melting point
Organic Functional Group
- Some Organic Compounds have functional groups. Some of them have 1 and some of them have more than 1. Functional group determines their chemical properties. Here are some Functional groups.
1.Hydroxyl : Hydroxyl grop has a structure of R-OH (R stands for Alkyl group) and needs an alkyl to be attached. Hydroxyl make compounds called Alcohols. Name the Alkyl first and then Alcohol of the prefix according to how many carbons and then -nol. Hydroxyl attracts water so most alcohols is water soluble. Smaller Hydroxyls is more water soluble. Don't Confuse with hydroxide. Hydroxyl is for organic compounds only, while hydroxide is a polyatomic ion (OH(-1)) for ionic compounds. Examples: CH3-OH is named Methyl Alcohol or Methanol, C2H5-OH is named ethyl Alcohol or ethanol. There are other alcohols such as Gylcerol (C3H8O3)

2. Aldehydes : Many organic compounds have aldehyde. Aldehydes have a structure of R-CHO Some Aldehydes have a strong odour. Smaller aldehydes is more water soluble. Naming aldehydes, ketones and Carboxyls are slightly different from hydrocarbon compounds by the prefixes of 1 carbon compound will be form- and 2 carbons compounds is acet-. Name the Prefix first by according to how many carbons and then aldehyde Counting carbons in aldehyde includes the carbon in the functional group. example CH2O is named Formaldehyde, CH3-CHO is named Acetaldehyde.

3. Ketones : Ketones have a very similar formula to aldehyde. It's Formula is R-CO-R', So there can be up to 2 alkyls in one Ketone. Counting Carbons for naming ketone does NOT include the carbon in the Functional Group. Name the Compound with ketone By prefix and then -one. Example : CH3-CO-CH3 is named Acetone.

4. Carboxyl : Carboxyl has a very similar formula to Aldehyde. It's Formular is R-COOH. Carboxyl produce compounds called Carboxylic acid. Counting carbon for naming includes carbon in the functional group. Name by prefix then -ic acid. Some of them have special name, Mostly Fatty acids dosen't have prefixes, they have a specific name. Carboxyl is also a functional group for fatty acid. Every acid with Caboxyl is considered Organic Acid. Most of them when dissociates give an ion. There is one special carboxylic acid, HCOOH is a carboxylic acid not aldehyde and it's named Formic Acid . Example : CH3COOH (Acetic Acid), C17H35COOH (Stearic Acid).

5. Sulfhydryl : Sulfhydryl has a structure of R-SH. Sulfhydryl produces a compound called Thiol. Sulfhydryl has a strong smell and some are not water soluble. Some Amino acid have sulfhydryl and 2 sulfurs can bond with each other to make a bond called Disulfide bond. Name the Sulfhydryl compound by Naming the alkyl and then thiol. Example: CH3SH (Methyl Thiol).

6.Amine : Amine has a structure of R-NH2 (Primary Amine). There are more structure of amine which is Secondary amine (R-NH-R') and tertiary amine (R-N(R')-R''). Amine makes many compound with other functional groups such as amino acids which is amine with carboxyl. All amino acids have a name. Amine also Acts as a base. If you are naming the amine compound with an alkyl, name the alkyl first then amine. Example : C2H5-NH2 (Ethyl Amine). Here are some amino acids : Alanine, Threonine.
.png) | ||||
Primary Amine
7.Organic Phosphate: Organic Phosphate have a structure of -PO4H2, Which is the similar to inorganic phoshate (PO4(3-)). Organic phosphates are usually found in ATP, Nucleic acid, DNA). Phosphate group can store a large amount of energy in their Bonds.
|

- Here are just some Basic Functional group, There can be more functional group, Some of them are combined function groups with other functional groups of hydrocarbons.





No comments:
Post a Comment