
- Here Are Some Links to Interactive Periodic tables.
http://www.ptable.com/

The elements in the periodic table are arranged by atomic number. The Scientist who invent the periodic table is Dmitri Mendeleev but his table is arranged by atomic mass. The Rows on the table are called Period, It tells how many shells of electrons. The Column are called Group, It tells how many Valence electron (Electrons on the outermost shell) for representative elements only (Column 1-2, 13-18) , The Element on Column 3-12 are Transition metals.
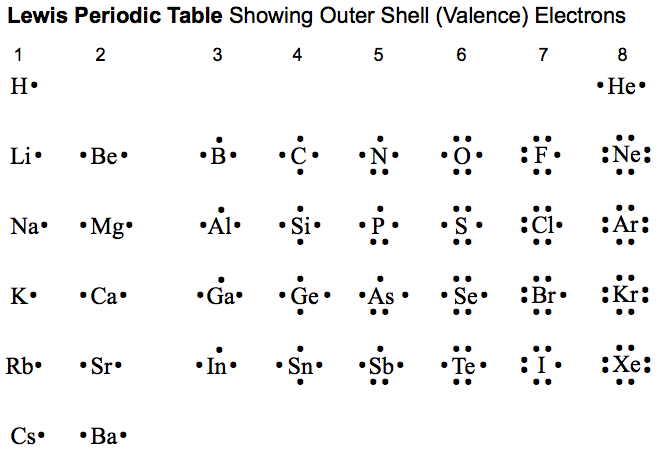
Here are the 8 Groups of representative elements/
- Group 1A : Alkali Metals. They all have 1 valence electron. They are very reactive and they react violently with water. They have a very low electro-negativity and ionization energy. Every ionic compound with alkali metals can dissolve in water. The reactivity increase as we go down the table. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +1 in ion state.


- Group 2A : Alkaline Earth Metals. They all have 2 valence electrons. They are not reactive as Alkali metals. They can react with water but some metal like Magnesium need steam in order to react. Not every ionic compounds with Alkaline Earth Metals can dissolve in water like Alkaline earth metal Sulfates Carbonates and Phosphates. The reactivity increase as we go down the table. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +2 in ion state.

- Group 3A (13) : Other Metals : Metalloids start to appear in this group. They All have 3 Valence electrons. They are not very reactive. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +3 in ion state.

- Group 4A (14) : The Carbon Family: Nonmetals starts to appear. They all have 4 Valence Electrons. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +/-4 in ion state.

- Group 5A (15) : The Nitrogen Family : They have 5 valence electrons. They start to get reactive. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +5 or -3 in ion state.
- Group 6A (16) : The oxygen Family or The Chalcogens: They have 6 valence electrons. They start to get more reactive then the nitrogen family. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +6 or -2 in ion state. The reactivity increases as we go up the table.
- Group 7A (17) : The Halogens: They have 7 valence electrons. They are very reactive. They have an oxidation number and a charge of +7 or -1 in ion state. They have a very high ionization energy and electronegativity. The reactivity increases as we go up the table.

- Group 8A (18) : The Noble Gases: They have full valence electrons (2 for Helium and 8 for other elements). They are very stable and they don't even react or some of it don't make a compound. They don't have an ion because they are very stable.


- Group 1-8B (3-12) : The Transition Metals: They can make more than 1 ions and there electron configuration are different from Representative elements. They have very similar characteristics if they are near each other in the table. Such as Gold, Platinum and Silver are Noble Metals and they have an extremely low reactivity.

- The Atomic radius and size of the atoms of the elements have a trend and pattern. As we go down and to the left, It's get bigger and in vice versa, As we go up and to the right, It's get bigger. So, Francium has the largest atom while Helium has the smallest atom.


Read Light Class 10 | SEE Physics Notes here
ReplyDelete